At our clinic there are a number of foot conditions and disorders that can be treated with the use of custom made orthotics. After a thorough physical assessment and computerized video gait analysis, we can educate you on the type of foot condition you may have and how custom made orthotics can help.
Many of the conditions result from poor or improper biomechanics of the foot and lower limb. Since the feet are the foundation for the rest of the body. Any imbalances in the feet can cause a chain reaction of events throughout the lower limb which can lead to any number of problems.
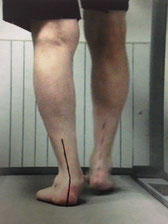
Pronation:
Pronation is the inward rolling of the foot during the gait cycle. The rolling in of the foot is to distribute the forces of impact during motion. In order for the foot to function normally, there must be an adequate amount of pronation (usually between 4-6 degrees). However when there is excessive pronation this can lead to a number foot related conditions that can cause discomfort.
Whenever excessive pronation occurs this often results in:
- internal rotation tibia (shin)
- abduction of the forefoot (feet pointing to the outside)
- internal rotation of the knee
- gene valgum (knocked knees)
- functional short leg
Any number of these abnormal motions puts pressure on other areas of the foot and throughout the lower limb that they aren't designed for, resulting in discomfort.
FOREFOOT VARUS DEFORMITY
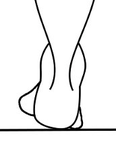
What leads the foot to excessively pronate usually has to do with the structure of the foot itself. When there is a forefoot varus deformity which is defined as the inverted position of the forefoot in relation to the rear foot (right) this causes the foot to compensate by increasing the amount of pronation so that medial side foot makes contact with the ground and allow the 1st metatarsal (big toe) to push off.
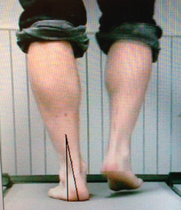
Supination:
Supination is the natural rolling out movement of the foot during the gait cycle. In early mid stance, when the subtalar joint stops pronating and begins to reverse its movement. Supination is a normal part of the gait cycle as it allows the foot to go from a mobile adaptor (pronation) to a rigid lever for propulsion.
When the foot excessively supinates it puts the foot in a less stable position to provide proper shock absorption. Excessive supination often leads to over-use type injuries as the pressure remains on the outside part of the foot longer than it should and puts the foot in a very vulnerable position which often leads to injury.
Whenever excessive supination occurs this often results in:
- external rotation of tibia (shin)
- adduction of the forefoot (pigeon toes)
- external rotation of the knee
- gene vacuum (bow legs)
